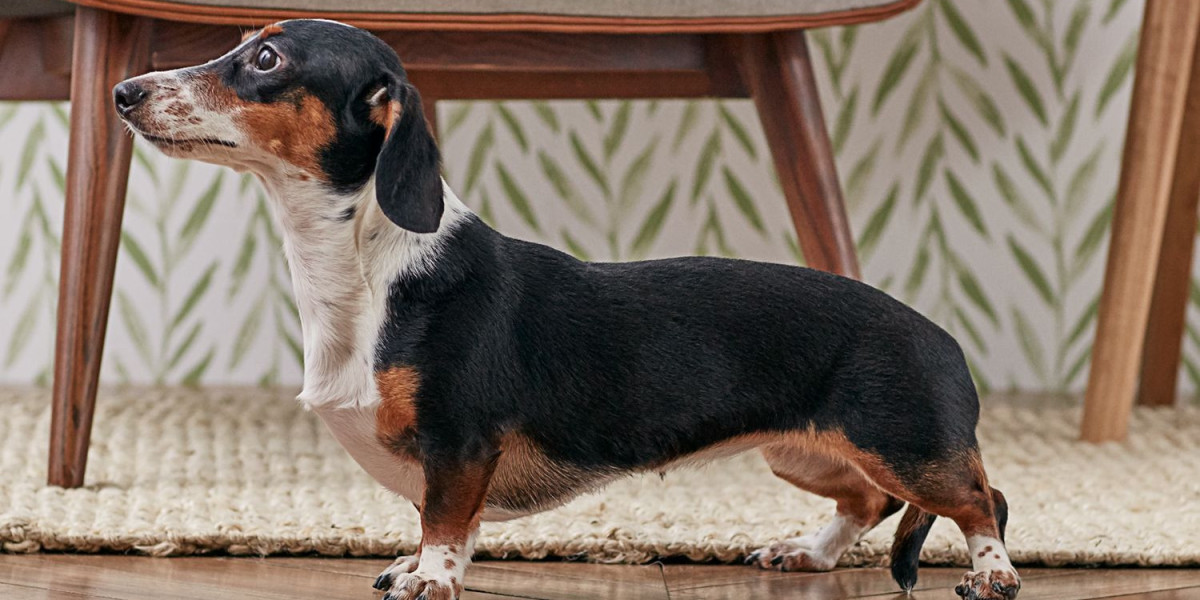
The Dachshund's long body is a characteristic feature that has been selectively bred for specific purposes. Dachshunds were originally developed in Germany several centuries ago, and their unique body shape was designed to enable them to excel in hunting small game, particularly badgers.
The long body and short legs of Dachshunds allowed them to easily enter and navigate the burrows of badgers, which are underground-dwelling animals. The breed's name, "Dachshund," translates from German to "badger dog." Their elongated bodies and strong, sturdy build were advantageous for pursuing badgers into their burrows and confronting them in tight spaces.
The three coat varieties of Dachshunds (smooth, long-haired, and wire-haired) all share this characteristic body shape. While the original purpose of Dachshunds was hunting, they have become popular companion animals due to their friendly temperament, intelligence, and distinctive appearance. The long body remains a defining trait of the breed, even in individuals that are not used for hunting purposes.
Historical Purpose
The long bodies of Dachshunds can be traced back to their historical purpose as hunting dogs in 17th-century Germany. Their name "Dachshund" even translates to "badger dog" in German. Bred to hunt and track burrow-dwelling animals such as badgers, their elongated bodies allowed them to easily enter and navigate underground tunnels. The unique shape of the Dachshund, with its long body and short legs, was specifically designed to excel in this type of hunting.
The elongated build helped them maneuver through tight spaces, while the short legs provided the strength needed to dig and pursue their prey. Over time, the distinctive physical characteristics of the Dachshund became a defining trait of the breed, even as their roles shifted from hunters to beloved companion animals.
Design for Tunneling
Dachshunds have long bodies primarily due to selective breeding for their original purpose as hunters of burrow-dwelling animals. The elongated design of their bodies, combined with short legs, was intended to facilitate their entry into narrow tunnels and burrows to pursue game such as badgers. This unique physique allowed them to navigate tight spaces underground with agility and efficiency.
The elongation of the body, coupled with a strong and muscular build, enhanced their ability to dig and maneuver through the intricate passageways of burrows. While today's Dachshunds may not necessarily engage in hunting as much, their distinctive body shape remains a testament to their historical role as skilled tunneling dogs.
Evolution of the Breed
Dachshunds, known for their distinctive long bodies and short legs, evolved over centuries to meet specific hunting needs. The elongated body allowed them to enter narrow burrows and tunnels, while their tenacious nature and acute sense of smell made them skilled hunters. The breed's development involved crossing various hound and terrier types, resulting in a compact yet elongated physique.
This unique body shape enhanced their ability to navigate underground passages and confront prey in confined spaces. The evolution of the dachshund's body is a testament to the breed's specialized function as a versatile and efficient hunting companion, characteristics that have persisted and contributed to their enduring popularity as beloved pets today.
Unique Aesthetic Appeal
Dachshunds' long bodies contribute to their unique aesthetic appeal by seamlessly blending form and function. Originating from Germany, these elongated canines were originally bred for their ability to navigate and hunt in narrow tunnels, a trait accentuated by their elongated bodies and sturdy legs. This distinctive physique not only reflects their historical purpose but also grants them a captivating and unconventional appearance.
Their elongated torsos, accompanied by short legs and expressive eyes, create a charming and endearing look that sets them apart from other breeds. The dachshund's long body serves both a practical and aesthetic purpose, embodying a harmonious fusion of specialized design and visual allure.
Health Considerations
Dachshunds have long bodies due to selective breeding that aims to create a breed specialized for hunting. Their elongated bodies and short legs were designed to facilitate burrowing into dens and tunnels to pursue prey. However, this unique body structure can pose health considerations, as dachshunds are prone to back problems such as intervertebral disc disease (IVDD) due to the strain on their spine.
Despite these health concerns, the distinctive appearance of dachshunds with their elongated bodies and charming personalities contribute to their enduring appeal as beloved companions, making them sought-after pets for those who appreciate their distinctive look and playful nature. Responsible breeding practices and proactive health care can help mitigate potential issues associated with their long bodies.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, the distinctive long bodies of Dachshunds can be attributed to their historical purpose as hunters. Originally bred in Germany to track and hunt burrow-dwelling animals such as badgers, the elongated body allowed them to maneuver through narrow tunnels and burrows with ease. This unique physical trait became a defining characteristic of the breed over time.
While their elongated bodies serve a functional purpose, it has also become a distinguishing feature that adds to the charm and individuality of these small, spirited dogs. Today, Dachshunds are beloved companions, and their long bodies continue to be a reminder of their fascinating heritage and specialized skills as skilled hunters.