In the realm of agriculture, technological advancements have always played a pivotal role in enhancing productivity, sustainability, and profitability. One such groundbreaking innovation that has garnered attention and acclaim is the Happy Seeder. Revolutionizing the way farmers approach crop residue management and conservation agriculture, the Happy Seeder stands as a beacon of hope for a more sustainable and efficient farming future.
Understanding the Happy Seeder
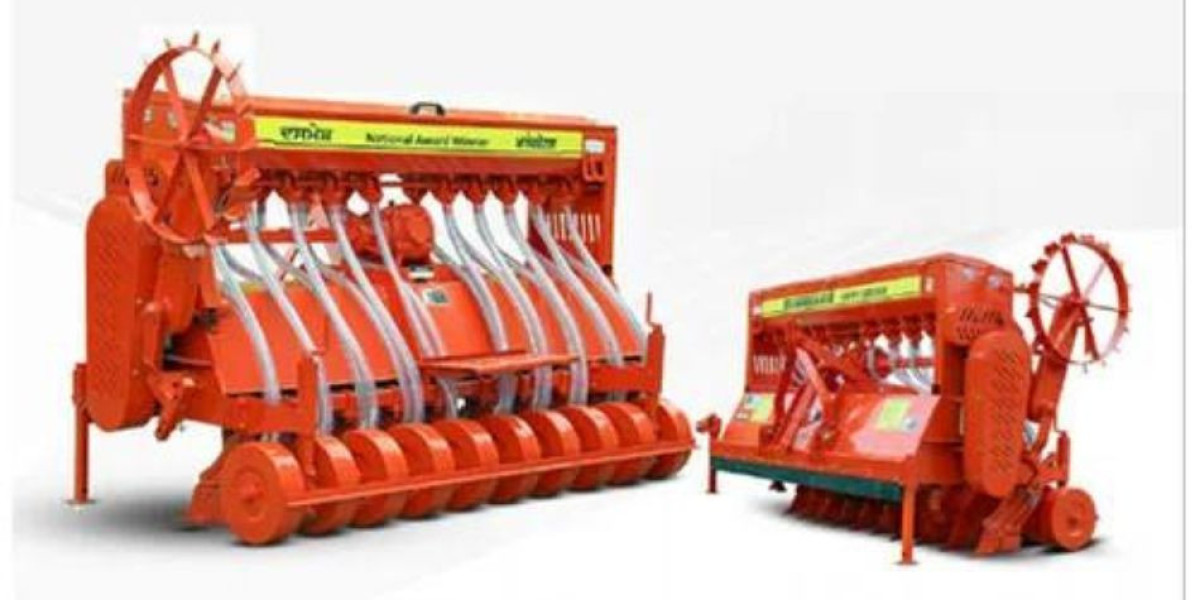
The Happy Seeder is a specialized agricultural machine designed to address the challenges associated with stubble burning, which has been a significant environmental concern in many agricultural regions worldwide. Stubble burning, the practice of setting fire to crop residues after harvest, contributes to air pollution, soil degradation, and climate change. The Happy Seeder offers a viable alternative by enabling farmers to sow seeds directly into the soil without the need for prior clearing of crop residues.
How Does it Work?
The Happy Seeder operates through a combination of processes that streamline the planting of new crops while simultaneously managing crop residues. Here's a brief overview of its functioning:
1. Residue Management: The Happy Seeder is equipped with components that allow it to cut and mulch crop residues left in the field after harvesting. This process chops the residues into smaller pieces, facilitating their incorporation into the soil.
2. Seed Placement: Simultaneously, the Happy Seeder sows seeds directly into the soil, utilizing the mulched crop residues as a natural mulch layer. This mulch layer helps in retaining soil moisture, suppressing weed growth, and improving soil health.
3. Minimal Soil Disturbance: Unlike traditional methods that involve intensive tillage, the Happy Seeder minimizes soil disturbance, preserving soil structure and reducing erosion. This aspect is crucial for maintaining soil fertility and sustainability over the long term.
Benefits of Happy Seeder Adoption
The widespread adoption of Happy Seeder technology brings forth a multitude of benefits, both for farmers and the environment:
1. Environmental Sustainability: By eliminating the need for stubble burning, the Happy Seeder significantly reduces air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. It also promotes soil conservation and biodiversity by preserving crop residues as natural soil amendments.
2. Improved Soil Health: The minimal soil disturbance and incorporation of crop residues enhance soil organic matter content, nutrient retention, and microbial activity. This leads to healthier soils that support robust crop growth and higher yields.
3. Water Conservation: The mulch layer formed by crop residues helps conserve soil moisture, reducing water evaporation, and enhancing water infiltration. This is particularly beneficial in regions facing water scarcity or erratic rainfall patterns.
4. Weed Suppression: The mulch layer acts as a natural weed suppressant, reducing the need for herbicides and manual weed control efforts. This not only saves costs for farmers but also promotes sustainable weed management practices.
5. Time and Cost Efficiency: By combining residue management and seeding operations into a single pass, the Happy Seeder saves time and labor for farmers. It also reduces the dependence on multiple pieces of equipment, leading to cost savings in the long run.
Challenges and Adoption Strategies
While the Happy Seeder offers promising solutions, its widespread adoption faces certain challenges that need to be addressed:
1. Awareness and Education: Many farmers may not be aware of the benefits of Happy Seeder technology or how to effectively integrate it into their farming practices. Educating farmers through training programs, demonstrations, and extension services is crucial for increasing adoption rates.
2. Financial Accessibility: The initial investment cost for purchasing a Happy Seeder and associated machinery can be a barrier for small-scale farmers. Government subsidies, financial assistance programs, and leasing options can make the technology more accessible to a wider range of farmers.
3. Technical Support and Maintenance: Ensuring access to reliable technical support, maintenance services, and spare parts is essential for maximizing the efficiency and longevity of Happy Seeder machines. Collaborative efforts involving government agencies, agricultural institutions, and private sector stakeholders can facilitate this support network.
4. Customization for Regional Variations: Agriculture practices vary across regions due to differences in soil types, cropping patterns, and climatic conditions. Customizing Happy Seeder designs and recommendations based on regional variations can enhance its relevance and effectiveness for diverse farming contexts.
Future Prospects and Conclusion
As the global agricultural landscape continues to evolve, innovations like the Happy Seeder pave the way for sustainable intensification, where productivity and environmental stewardship go hand in hand. The integration of precision agriculture technologies, data-driven insights, and farmer-centric approaches will further enhance the impact and scalability of Happy Seeder adoption.
In conclusion, the Happy Seeder represents a transformative solution that addresses pressing environmental challenges while empowering farmers with efficient and sustainable agricultural practices. Embracing such technologies not only secures food production for future generations but also fosters a harmonious relationship between agriculture and the environment.