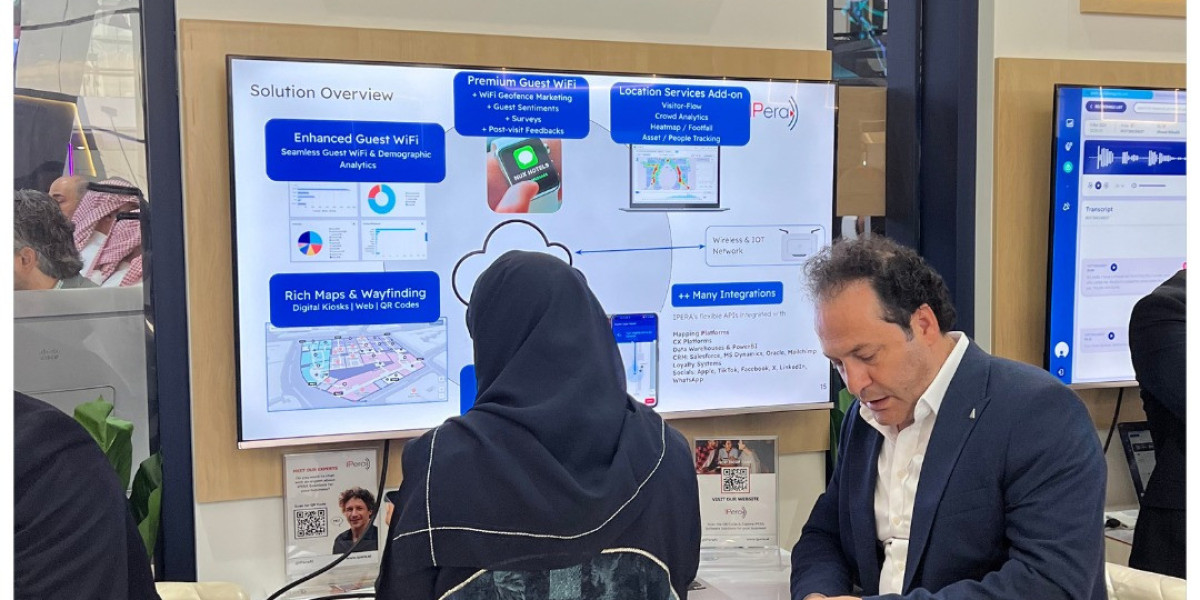
Finding our way through busy indoor spaces can often be challenging. Traditional methods of navigation, such as paper maps or static signage, are becoming outdated in the face of modern technology. That's where indoor navigation systems come in, revolutionizing the way we move through indoor spaces with precision and ease.
IPERA.AI - Indoor Wayfinding for Hospitals from IPERA AI on Vimeo.
Understanding Indoor Navigation Systems
Indoor navigation systems use a combination of advanced technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, RFID, and magnetic positioning to provide real-time guidance to users within indoor environments. By integrating these technologies with sophisticated mapping algorithms, indoor navigation systems can offer turn-by-turn directions, points of interest, and even personalized recommendations based on user preferences.
How do indoor navigation systems work?
The systems use intricate algorithms that process data from various sources to determine a user's location and guide them to their destination. Wi-Fi signals are used to triangulate a user's position within a building, while Bluetooth beacons and RFID tags can also pinpoint a user's location with precision. Magnetic positioning is used to determine a user's orientation and direction of movement, especially in environments where GPS signals are unreliable or unavailable.
1. Wi-Fi Positioning: Wi-Fi signals are used to triangulate a user's position within a building. By analyzing signal strength and the proximity to access points, indoor navigation systems can estimate the user's location with high accuracy.
2. Bluetooth Beacons: Bluetooth beacons are small devices placed strategically throughout indoor spaces. These beacons emit signals that can be detected by users' smartphones or other devices equipped with Bluetooth capabilities. By recognizing the unique identifiers of these beacons, indoor navigation systems can pinpoint a user's location with precision.
3. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification): RFID technology utilizes electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. In indoor navigation, RFID tags can be embedded in assets or placed at key locations to aid in navigation and wayfinding.
4. Magnetic Positioning: Magnetic positioning relies on the Earth's magnetic field to determine a user's orientation and direction of movement. By analyzing changes in magnetic field strength, indoor navigation systems can provide accurate directional guidance, especially in environments where GPS signals are unreliable or unavailable.
The Benefits of Indoor Navigation Systems
Indoor navigation systems offer a myriad of benefits for both users and businesses. By providing seamless navigation and wayfinding assistance, indoor navigation systems improve the overall user experience within complex indoor environments. Businesses can optimize operations and improve efficiency by streamlining visitor flow, reducing congestion, and guiding customers to their destinations more efficiently. This can lead to higher customer satisfaction and increased revenue opportunities.
1. Enhanced User Experience: By providing seamless navigation and wayfinding assistance, indoor navigation systems improve the overall user experience within complex indoor environments. Users can navigate with confidence, saving time and reducing frustration.
2. Increased Efficiency: Businesses can optimize operations and improve efficiency by streamlining visitor flow, reducing congestion, and guiding customers to their destinations more efficiently. This can lead to higher customer satisfaction and increased revenue opportunities.
3. Personalized Recommendations: Indoor navigation systems can analyze user preferences and behavior to offer personalized recommendations for nearby amenities, promotions, or points of interest. This personalized approach enhances engagement and fosters customer loyalty.
4. Accessibility: Indoor navigation systems can also benefit individuals with disabilities by providing tailored navigation assistance and accessibility information, ensuring that everyone can navigate indoor spaces independently and safely.
Real-World Applications
The versatility of indoor navigation systems makes them invaluable across a wide range of industries:
1. Retail: In retail environments, indoor navigation systems can guide shoppers to specific products, highlight promotions, and provide indoor mapping for large shopping centers or department stores.
2. Healthcare: Hospitals and medical facilities can utilize indoor navigation to help patients, visitors, and staff navigate complex layouts, locate departments or clinics, and find essential amenities.
3. Transportation: Airports, train stations, and other transportation hubs can benefit from indoor navigation systems to assist travelers in finding gates, check-in counters, baggage claim areas, and other facilities.
4. Corporate Environments: Large office buildings can implement indoor navigation systems to help employees and visitors navigate between floors, meeting rooms, and other facilities efficiently.
Looking Ahead
As technology continues to advance, indoor navigation systems are poised to become even more sophisticated and pervasive. Machine learning algorithms, augmented reality (AR), and indoor positioning technologies are driving innovation in this field, offering new possibilities for indoor navigation and wayfinding.