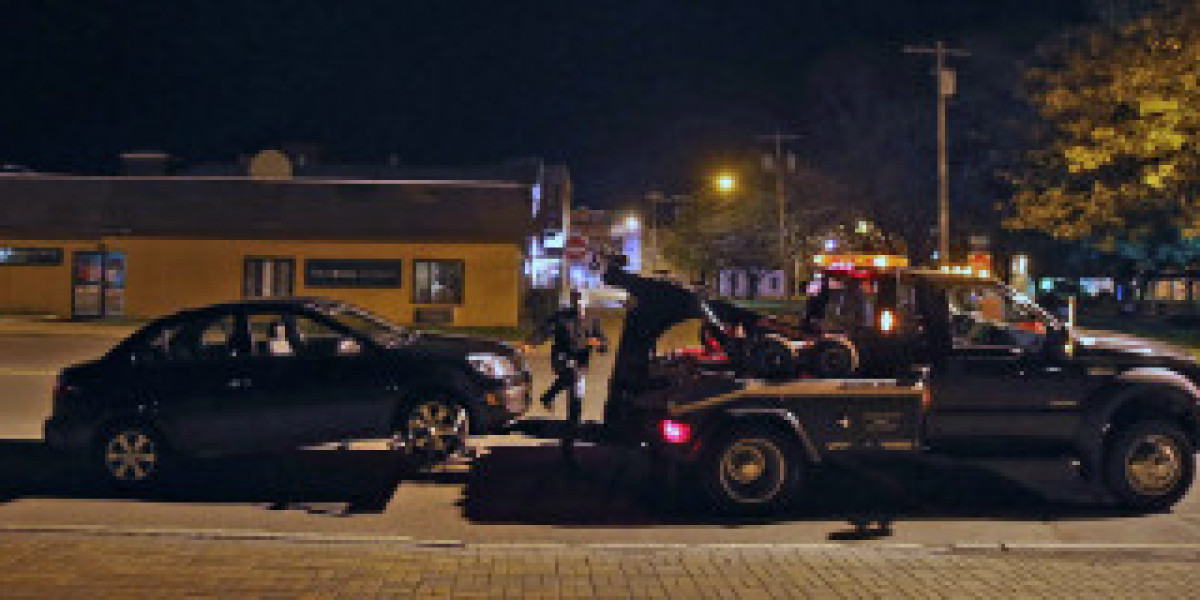
In today’s economy, where financial pressures and unexpected expenses can strain household budgets, the risk of car repossession is a reality for many. Whether you’ve fallen behind on payments or are simply curious about how the process works, understanding car repossession can help you navigate this challenging situation. In this blog post, we'll break down the essentials of car repossessions, from the reasons behind them to the legalities involved and tips for managing the situation.
What Is Car Repossession?
Car repossession occurs when a lender takes back a vehicle due to the borrower’s failure to meet the terms of the loan agreement. This usually happens when a borrower defaults on their auto loan payments. The repossession process is typically initiated by the lender or a collection agency hired by the lender.
Why Do Car Repossessions Happen?
- Missed Payments: The most common reason for repossession is missed or late payments. Auto loans are structured to ensure that the borrower makes regular payments over a specified term. Failure to meet these payments can lead to repossession.
- Unemployment or Financial Hardship: Situations such as job loss, medical emergencies, or other financial difficulties can make it challenging to keep up with loan payments.
- Divorce or Separation: Sometimes, changes in personal circumstances like divorce or separation can lead to financial instability and, subsequently, repossession.
- Bankruptcy: Filing for bankruptcy can sometimes lead to repossession, especially if the bankruptcy proceedings affect the borrower’s ability to continue payments.
The Repossession Process
- Default Notification: Before repossession occurs, the lender typically sends a notice of default. This document informs you that you are behind on payments and outlines the steps you need to take to remedy the situation.
- Repossessor's Role: If you fail to make the required payments or communicate with the lender, the repossession process may begin. A repossession agent or company is hired to locate and repossess the vehicle. Their role is to recover the vehicle without breaching the peace or engaging in illegal activities.
- Seizure of Vehicle: The repossession agent will attempt to seize the vehicle. This can happen at your home, workplace, or other locations where the vehicle is parked. The repossession must be done in accordance with the law—meaning the agent cannot break into a locked garage or use force.
- Post-Repossession: Once the vehicle is repossessed, it is usually taken to a storage facility. The lender will then sell the vehicle at an auction. The sale proceeds are used to pay off the outstanding loan balance. If the sale amount is less than the balance owed, the borrower may be responsible for paying the difference, known as a deficiency balance.
Legal Aspects of Repossession
- Right to Cure: In many states, borrowers have the right to “cure” the default before repossession. This means you can make up for missed payments and any associated fees to prevent the vehicle from being repossessed.
- Notice Requirements: After repossession, lenders are typically required to notify borrowers of the upcoming sale of the vehicle. This notice must include details about how to redeem the vehicle or how to contact the lender if you want to reinstate the loan.
- Auction and Deficiency: The lender must sell the vehicle in a commercially reasonable manner, usually through an auction. If the sale does not cover the full amount of the loan, the borrower may be liable for the remaining balance. However, laws vary by state, and some states have protections that may reduce or eliminate deficiency judgments.
- Repossession Laws: Repossession laws and procedures vary by state, so it’s important to understand the regulations specific to your location. Consulting with a legal expert can provide guidance tailored to your situation.
How to Avoid Car Repossession
- Communicate with Your Lender: If you’re facing financial difficulties, contact your lender as soon as possible. Many lenders are willing to work out a payment plan or provide temporary relief.
- Explore Refinancing: Refinancing your loan may result in lower monthly payments, making it easier to stay current on your loan.
- Create a Budget: Developing a detailed budget can help you manage your finances and prioritize essential expenses like loan payments.
- Seek Financial Counseling: Nonprofit credit counseling agencies can offer advice on managing debt and improving your financial situation.
What to Do if Your Car Is Repossessed
- Understand Your Rights: Familiarize yourself with the repossession laws in your state to ensure that the repossession was conducted legally.
- Review Your Loan Agreement: Check the terms of your loan agreement to understand any potential liabilities or obligations related to the repossession.
- Contact the Lender: Reach out to the lender to discuss the next steps. You may be able to negotiate a settlement or work out a payment plan for any remaining deficiency balance.
- Consider Legal Assistance: If you believe the repossession was conducted improperly or you need help negotiating with your lender, consider consulting a lawyer specializing in consumer law.
After Repossession: Rebuilding Your Financial Health
- Check Your Credit Report: Repossession will impact your credit score. Regularly review your credit report to ensure that the information is accurate and to track your progress in rebuilding your credit.
- Work on Improving Your Credit Score: Focus on paying down other debts, making timely payments, and avoiding new credit inquiries to gradually improve your credit score.
- Save for the Future: Building an emergency fund can help you manage unexpected expenses and reduce the risk of future financial difficulties.
Conclusion
Car repossessions is a serious matter that can have lasting effects on your financial well-being and credit score. Understanding the process, knowing your rights, and taking proactive steps to manage your finances can help you navigate this challenging situation. If you find yourself facing repossession, remember that seeking professional advice and exploring all available options can make a significant difference in the outcome. By addressing the issue head-on and making informed decisions, you can work towards financial stability and recovery.