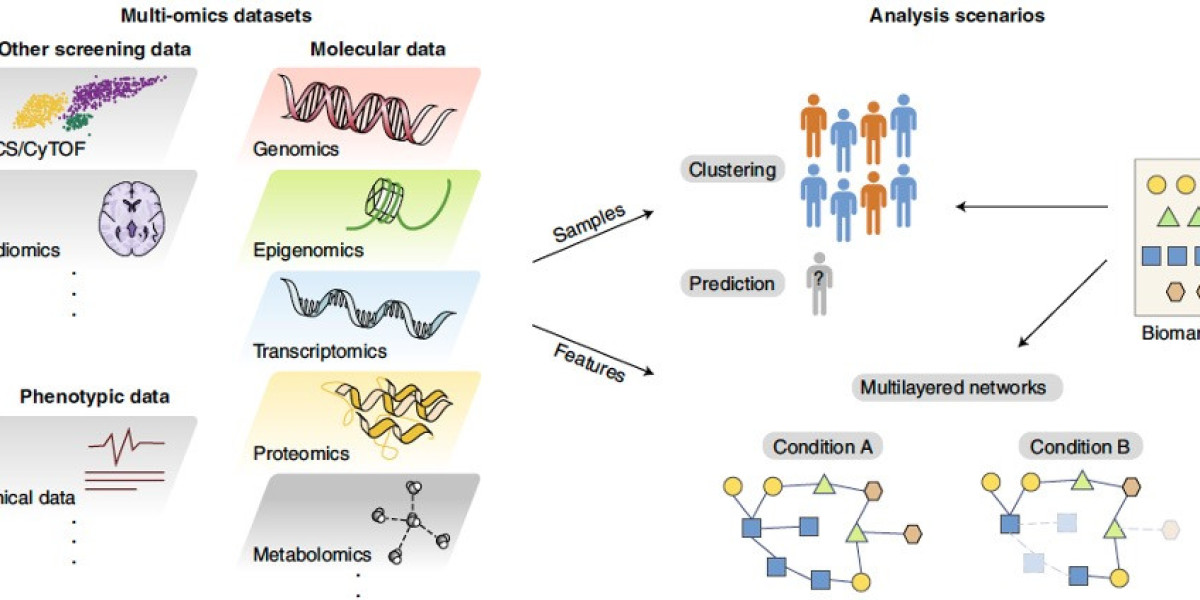
These "omics" layers provide a more complete view of biological systems than a single omics approach alone. By combining different types of data, researchers can gain valuable insights into molecular interactions, regulatory networks, and molecular pathways involved in biological processes and disease. In this article, we will explore the field of multi-omics and some of its current applications and potential to advance biological research globally.
Genomics and Multiomics Industry
Genomics provides the foundational layer of information by determining the complete DNA sequence of genomes. Multiomics However, the genome alone does not determine phenotype - there are complex regulatory layers on top of the genome that influence which genes are expressed. Multi-omics integrates genomic data with other omics layers like epigenomics and transcriptomics to provide a more comprehensive understanding of how the genome functions. Epigenomics studies mechanisms like DNA methylation and histone modifications that regulate genome activity and expression without altering the DNA sequence. Combining genomics with epigenomics can reveal how epigenetic changes modulate gene activity and expression patterns in health and disease. Transcriptomics profiles gene expression levels through RNA sequencing. Integrating genomics with transcriptomics can help identify genetic variations that influence gene regulation and expression variation between individuals or in response to environmental stimuli or disease states.
Proteomics and Metabolomics in Multi-Omics
While genomics, epigenomics and transcriptomics provide information on the genome and its regulation of gene expression, proteomics and metabolomics capture functional downstream readouts of these upstream layers. Proteomics studies all the proteins expressed in a biological system using techniques like mass spectrometry. It provides insight into how the genome and transcriptome are translated into the functional proteome. Similarly, metabolomics profiles small molecule metabolites that are substrates and products of metabolic reactions using technologies like NMR and mass spectrometry. These reveal functional consequences of changes at the genetic, epigenetic and gene expression levels. Combined multi-omics integrating proteomics and metabolomics with other layers can help map how genetic and expression changes propagate through molecular networks to influence phenotypes and health outcomes. This is proving useful for applications like biomarker and drug target discovery by providing a system-level view of disease pathogenesis.
Get more insights on - Multiomics